Jelastic PaaS provides automatic clusterization for the MongoDB stack, which allows you to create a reliable replica set for your database with a single click. The implemented solution provides a set of benefits:
- redundancy and data high availability - multiple copies of data on different database servers offer a high level of fault tolerance against the data loss
- scalability and autodiscovery – new nodes, added during horizontal scaling, are connected to the cluster with all required adjustments being applied automatically
- automated failover – the database nodes that are temporarily unavailable or have high latency are automatically excluded from the cluster and re-added once the connection is restored
All these benefits can be achieved just in a few clicks within a topology wizard. Explore the steps below to activate auto-clustering for your MongoDB database in Jelastic PaaS.
Specifics of the MongoDB Auto-Clustering
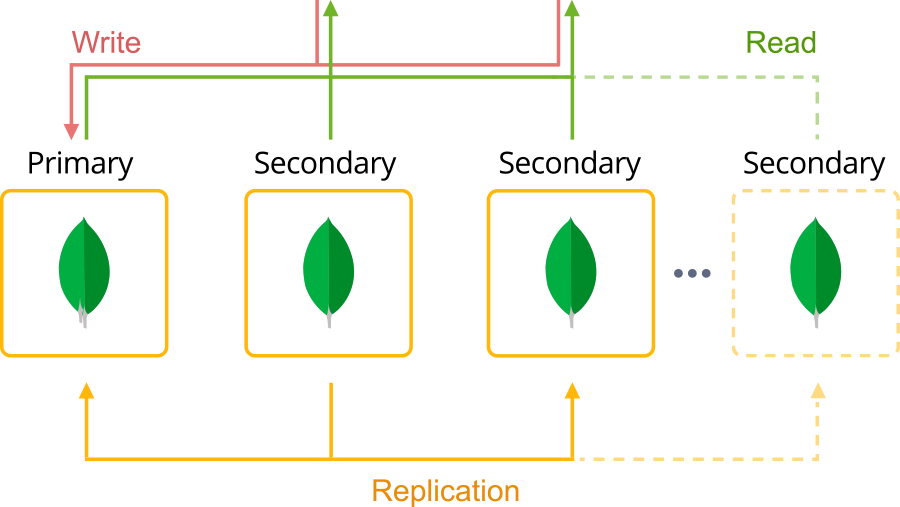
A replica set is a group of at least three MongoDB instances that maintain the same data. One node of the set is deemed primary and is responsible for all write operations. It records all changes in the oplog so that the remaining nodes (secondaries) can accurately reflect the primary’s data. If the primary becomes unavailable, a new one will be automatically elected from the active secondaries after a short delay.
The default values for the settings of the automatically configured cluster are provided below:
- "chainingAllowed" : true - allows secondary members to replicate from other secondaries
- "heartbeatIntervalMillis" : 2000 - the frequency in milliseconds for the heartbeats
- "heartbeatTimeoutSecs" : 10 - timeout in seconds that the replica set members wait for a successful heartbeat before marking the appropriate node as inaccessible.
- "electionTimeoutMillis" : 10000 - timeout in milliseconds for detecting if the primary member is unreachable
- "catchUpTimeoutMillis" : -1 - timeout in milliseconds (-1 for infinite time) for the newly elected primary to catch up with the members that have more recent writes
- "catchUpTakeoverDelayMillis" : 30000 - timeout in milliseconds a secondary node, that is ahead of the current primary, gives for the catchup before initiating election to become a new primary
Another important point is security and protection from undesired access. Herewith, authentication is an important security assurance process that forces each member of the replica set to identify itself during the internal communication by means of a special unique authentication key file. The platform automatically applies required configurations (in /etc/mongod.conf) and generates a key (located at /home/jelastic/mongodb.key) during the cluster configuration. Also, to ensure consistency, the file is added to the redeploy.conf file so that it remains through all the container lifecycle operations.
MongoDB utilizes the WiredTiger storage engine by default. It ensures a high performance (due to non-locking algorithms) and effective cost/resource utilization. The default options for WiredTiger are optimized to run a single mongod instance per server, which is also suitable for Jelastic PaaS containers. MongoDB utilizes both the WiredTiger internal cache and the filesystem cache. The internal cache size is 50% of total RAM minus 1 GB (but no less than 256 MB), while filesystem cache operates free memory that is not used by WiredTiger or other processes. For more information on WiredTiger configs, refer to the official MongoDB documentation.
One more unique feature of the MongoDB auto-cluster is the automated detection of new nodes added through the horizontal scaling and their inclusion into the replica set without any manual actions. Similarly, nodes are excluded from the cluster while scaling in.
Enable Automatic Clustering for Databases
The whole process of the MongoDB auto-cluster creation can be done in a few simple clicks.
1. Open the topology wizard with the New Environment button at the top-left corner of the dashboard, choose MongoDB database, and activate Auto-Clustering via the appropriate switcher.
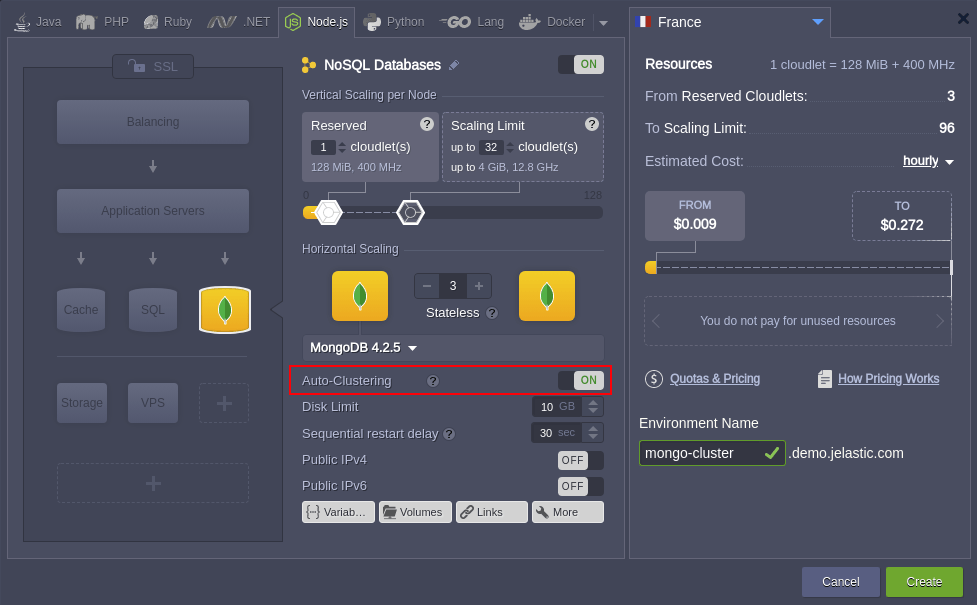
- auto-clustering is supported since the 4.x.x version
- 4 GiB of RAM (32 cloudlets) are recommended for a proper work of the replica set nodes. By default, these number of cloudlets are added as a dynamic scaling limit, so you won’t be charged unless resources are actually consumed.
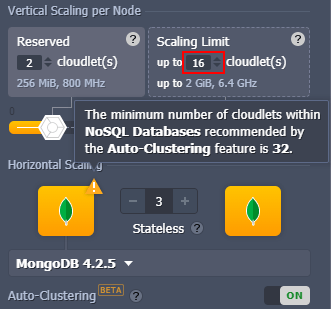
- the minimum number of nodes required for the MongoDB auto-cluster is 3
Configure other parameters up to your needs (public IPs, region, etc.) and click Create.
2. Wait a minute for the platform to configure the cluster for you.
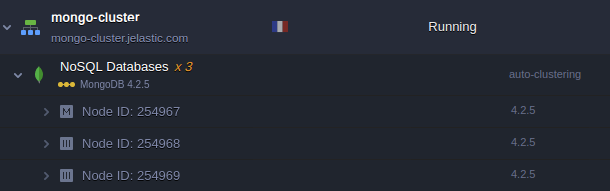
3. After successful installation, you’ll receive an email about successful replica set configuration:

You can use these credentials to access the admin panel or to establish connections from your applications to the primary node of the replica set.
Here is the connection string example in case of node.js application:
client = new MongoClient("mongodb://admin:L3tdH8bT64@node254967-mongo-cluster.jelastic.com:27017,node254968-mongo-cluster.jelastic.com:27017,node254969-mongo-cluster.jelastic.com:27017/admin", {useUnifiedTopology: true, readPreference:'primaryPreferred',replicaSet:'rs0'});
Where:
useUnifiedTopology: true - forces mongodb to use the new Server Discover and Monitoring engine.
readPreference:'primaryPreferred' - Mostly, operations read from the primary but if it is unavailable, operations read from secondary members.
replicaSet:'rs0' - by default the replica set name is rs0 in Jelastic. You may observe the replica set name at any cluster node in mongod.conf file or in mongo shell prompt.
The outlined above application connection is considered to be established within one hosting platform. But if required, you can make an external application connection to the replica set through SLB. In this case you have to maintain connection to the primary node only for read/writes via Jelastic Endpoints.
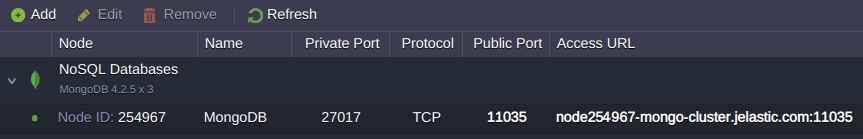
If you need to read from the secondaries you have to customize your application code to perform reading from secondaries in a separate thread as you do it for primary. Anyway, for such cases, you have to remove replicaSet parameter from the connection string so it can look according to email above:
client = new MongoClient( "mongodb://admin:L3tdH8bT64@node254967-mongo-cluster.jelastic.com:11035/admin", { useUnifiedTopology: true });
4. By default, the auto-cluster utilizes the Mongo Express administration panel that provides support for the replica sets.
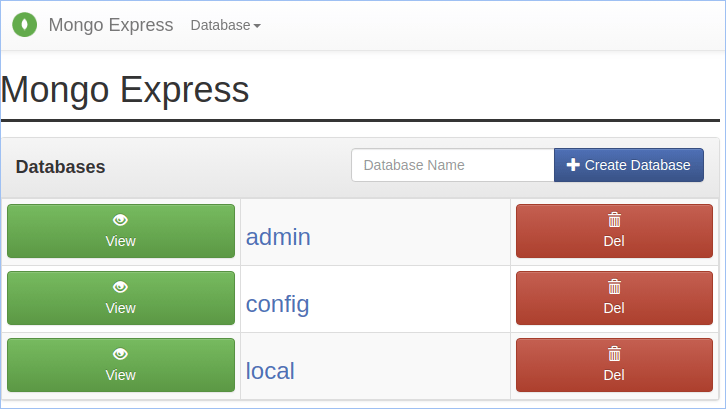
5. Also, you can connect to your database via the mongo shell directly in your terminal (for example, using the built-in Web SSH option).
mongo -u {user} -p {password} {DB_name}
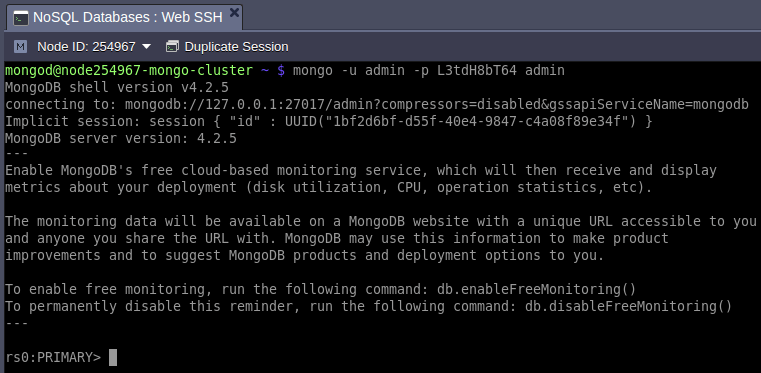
Where:
- {user} – administrator username (sent to your email, admin by default)
- {password} – password for the corresponding DB user (can be found within the same email)
- {DB_name} – name of the database you would like to access (we’ll use the default admin one)
6. You can check the replica set status with the appropriate command:
rs.status()
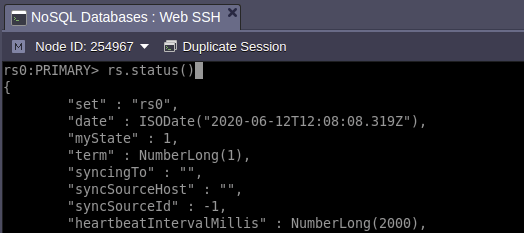
As you can see, the replica set (with the default rs0 name) is up and running. Other replica set commands can be found at the official documentation. For example, use the rs.conf() operation if you want to see replica set configs.
Get your own highly-available MongoDB replica set with Jelastic PaaS at one of the service providers.