PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source SQL database with the object-relational structure and numerous robust features to ensure excellent performance and reliability. In this tutorial, we’ll show how to connect PostgreSQL database with Java application hosted with Jelastic PaaS.
1. Log into Jelastic dashboard, create New Environment with the Java application server and the PostgreSQL database.
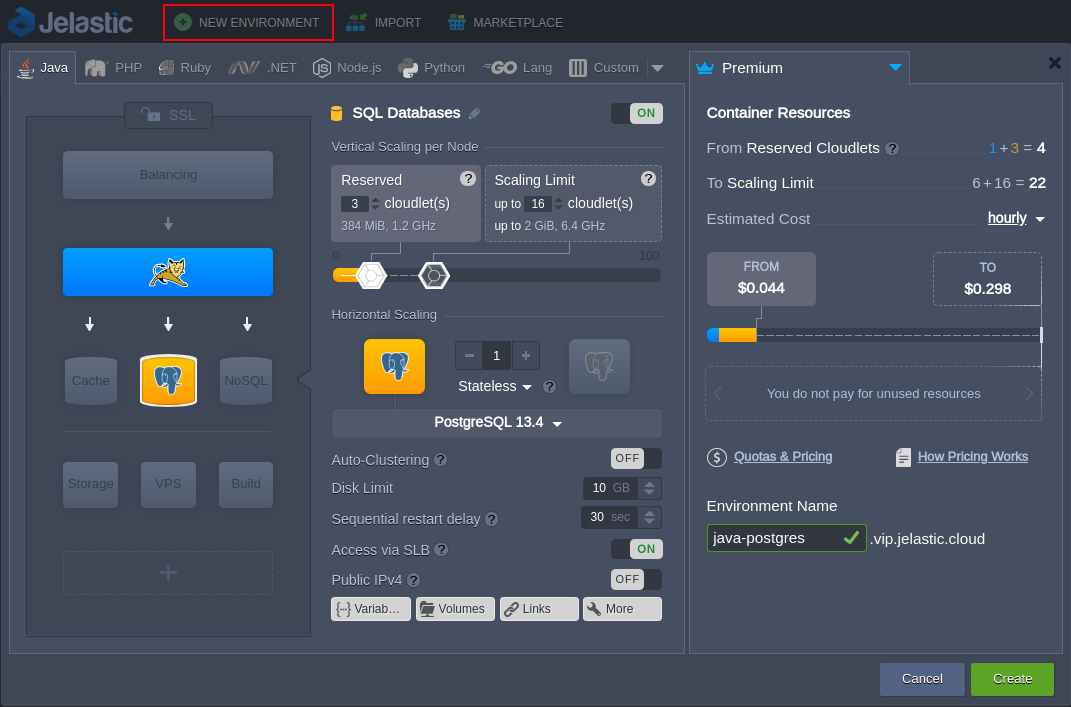
2. After creation, you’ll receive an email with your database access credentials (host, login, and password).
3. Click the Config button next to your application server (Tomcat in our case) to access the configuration file manager and create a new mydb.cfg file in the /opt/tomcat/temp folder.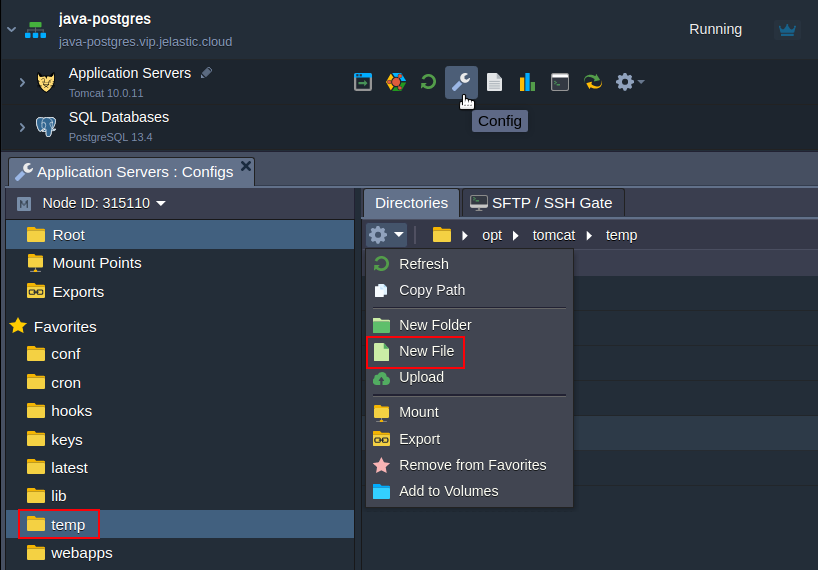
4. Provide the following connection details in the mydb.cfg file:
host=jdbc:postgresql://{host}/{db_name}
username={user}
password={password}
driver=org.postgresql.Driver
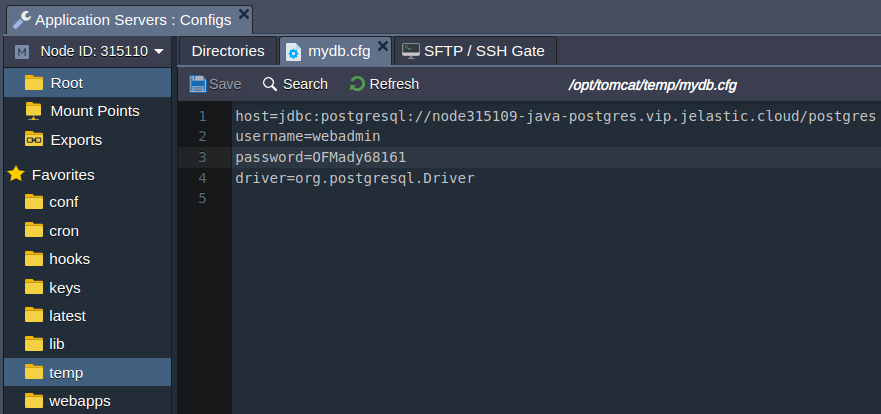
Here:
- {host} - link to your DB node without protocol part
- {db_name} - name of the database (postgres in our case)
- {user} and {password} - admin user credentials
However, for this example, we’ll take the default user (i.e. webadmin with full administrative access to the server) and database (postgres).
5. Below, you can see the code of the application used in this tutorial.
package connection;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class DbManager {
public String date = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy-HH-mm").format(new Date());
private final String createTable = "CREATE TABLE \"" + date + "\" (id INT, data VARCHAR(100));";
private static final int LoginTimeout = 10;
public DbManager() {
}
public Connection createConnection() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
System.out.println("\n\n=======================\nJDBC Connector Test " + date);
System.out.println("User home directory: " + System.getProperty("user.home"));
String host;
String username;
String password;
String driver;
try {
prop.load(new java.io.FileInputStream(System.getProperty("user.home") + "/mydb.cfg"));
host = prop.getProperty("host").toString();
username = prop.getProperty("username").toString();
password = prop.getProperty("password").toString();
driver = prop.getProperty("driver").toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Unable to find mydb.cfg in " + System.getProperty("user.home") + "\n Please make sure that configuration file created in this folder.");
host = "Unknown HOST";
username = "Unknown USER";
password = "Unknown PASSWORD";
driver = "Unknown DRIVER";
}
System.out.println("host: " + host + "\nusername: " + username + "\npassword: " + password + "\ndriver: " + driver);
Class.forName(driver);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.println("DRIVER: " + driver);
System.out.println("Set Login Timeout: " + LoginTimeout);
DriverManager.setLoginTimeout(LoginTimeout);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(host, username, password);
System.out.println("CONNECTION: " + connection);
return connection;
}
public String runSqlStatement() {
String result = "";
try {
Statement statement = createConnection().createStatement();
System.out.println("SQL query: " + createTable);
statement.execute(createTable);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(DbManager.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
System.out.println("Exception occurred: " + ex);
result = ex.getMessage();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
result = ex.getMessage();
}
return result;
}
}
6. Deploy our example application to your Tomcat server. Due to different version servlet specifications supported by Tomcat 9 and Tomcat 10 we have prepared the respective applications:
For Tomcat 9: https://download.jelastic.com/public.php?service=files&t=18753849900d2461b3162bd4355f834d&download
For Tomcat 10: https://download.jelastic.com/public.php?service=files&t=503e9768ee573fd452cec8a34a2215b2&download
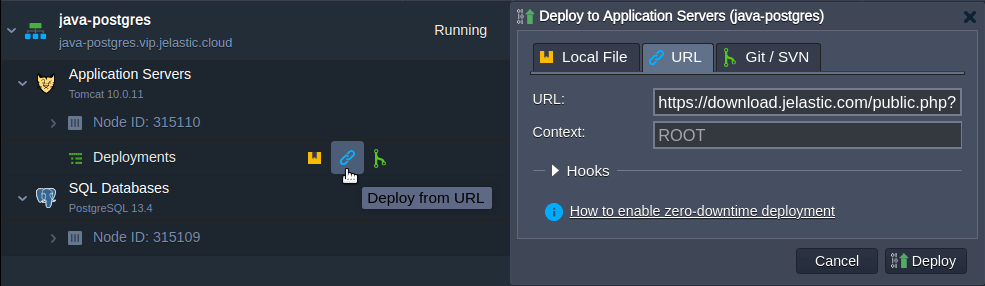
7. After successful deployment, click Open in Browser next to your application server.
8. Within the opened browser tab, click the Create test table in your database button.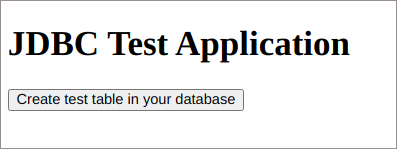
Your request will be processed shortly displaying the result message.

9. Let’s access our database via phpPgAdmin to ensure that a new table was created (access credentials are provided via the email described in the second step of this guide).
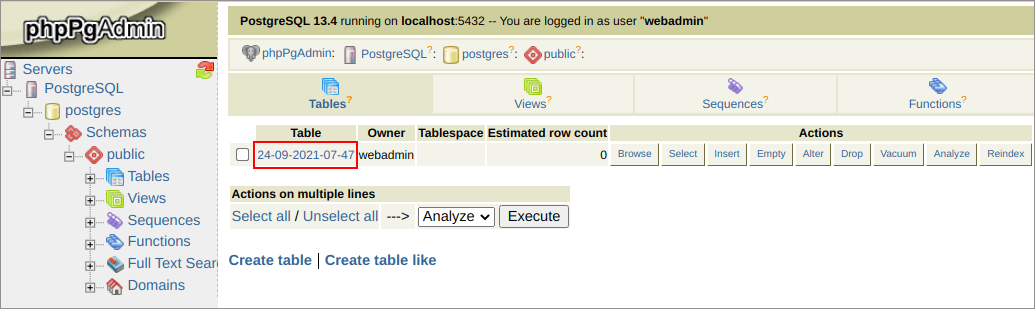
As you can see, a new table (named due to the date and time of the creation) has been successfully added by our Java application. The connection is successfully established! Try it out at one of the globally-available Jelastic service providers.
Related Articles
PostgreSQL Auto-Clustering with Asynchronous Master-Slave Replication
Establish Secure SSL Connection to PostgreSQL Database Server
How to Install Hasura GraphQL Engine for PostgreSQL-Based Applications