Database Configuration Files
In this guide, we’ll list all the main configuration files in the platform-managed database servers. Each line of the table corresponds to the folder with configs for the databases listed in the Database Types column.
| Folder | Path | Database Types |
|---|---|---|
| conf | /var/lib/pgsql/data | PostgreSQL |
| etc | /etc | all |
| cron | /var/spool/cron | all |
| scripts | /var/lib/jelastic/bin | all |
| backup | /var/lib/jelastic/backup | all |
| keys | /var/lib/jelastic/keys | all |
| conf.d | /etc/httpd/conf.d | MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, PostgreSQL |
ETC
The PHP configurations are performed in the php.ini file, which is located in the etc folder.
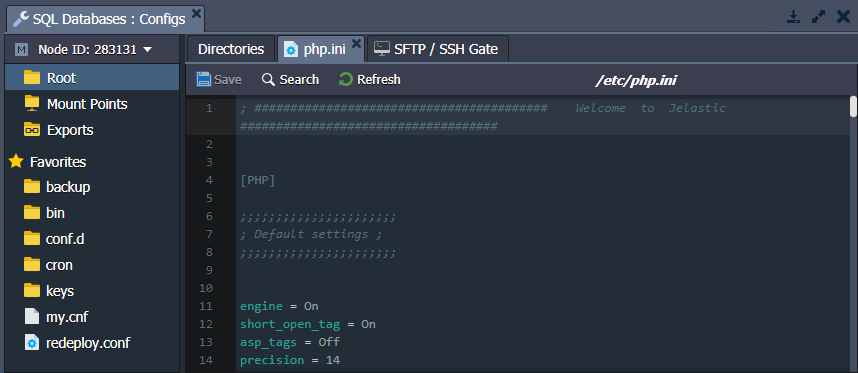
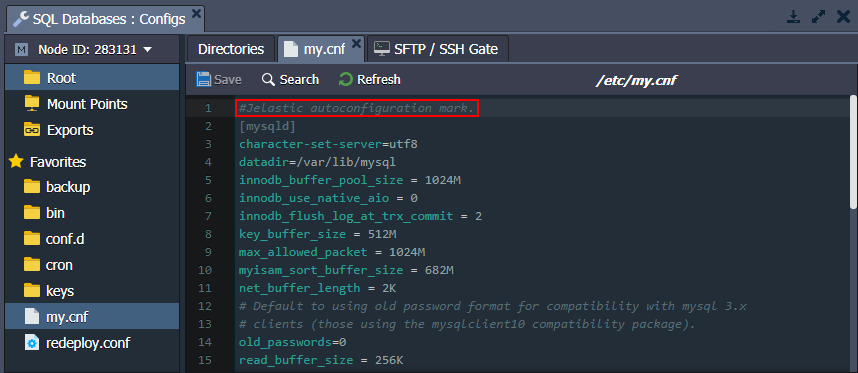
MySQL, MariaDB and Percona include the my.cnf configuration file for database management. Note that the platform automatically manages the following settings in this file:
- key_buffer_size
- table_open_cache
- myisam_sort_buffer_size
- innodb_buffer_pool_size
If you want to manually change any of the settings from the list above, you need to remove the “#Jelastic autoconfiguration mark.” line at the start of the file. Otherwise, your custom changes will be overwritten.
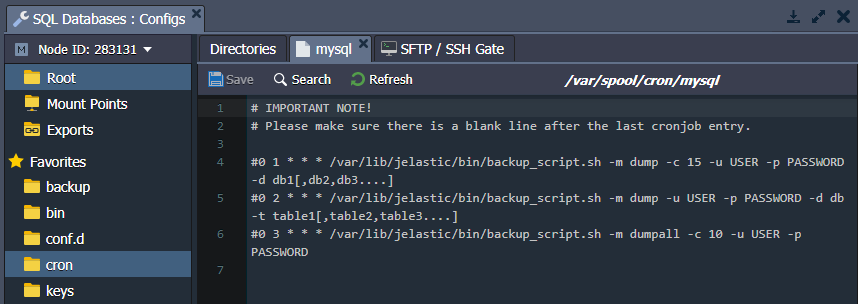
CRON
The database servers include the /var/spool/cron folder with a config file, where cron jobs can be configured.
For example, you can set the scheduled backups of your database. The required cron expression is included in the cron config file by default. You just need to uncomment the appropriate line and, if necessary, adjust it based on your custom requirements.
You can find more information in the Setting Up Cronjob documentation.
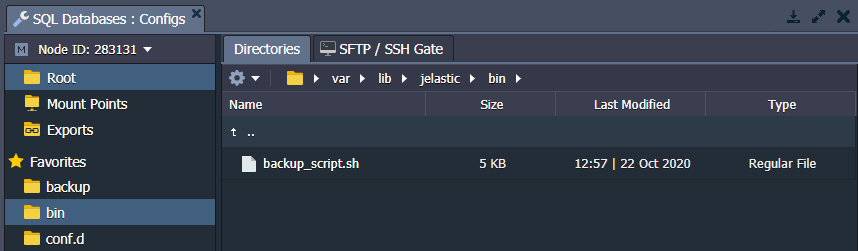
SCRIPTS
This folder contains the default backup_script.sh script. You can also use the /var/lib/jelastic/bin folder for uploading your custom scripts.
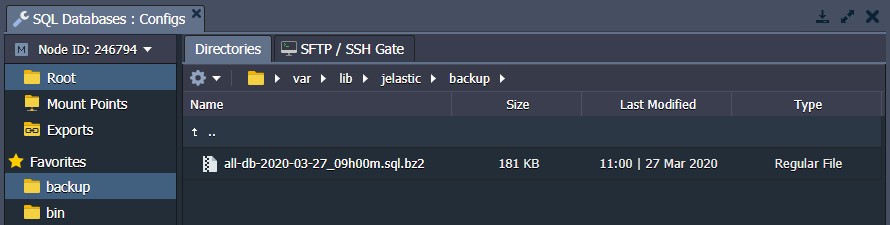
BACKUP
The /var/lib/jelastic/backup folder is used for storing the database backup files. You can use these files for restoring your database data.
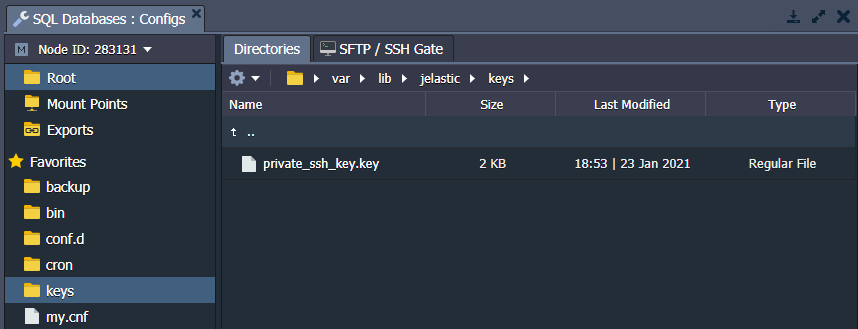
KEYS
The /var/lib/jelastic/keys directory is used as a location for uploading private keys that are needed for your application.
Generate the key, save it as a simple file, and upload it to the keys folder. You can then use it for different cases by merely stating the path to your key, i.e. /var/lib/jelastic/keys/{keyName}.
CONF.D
The /etc/httpd/conf.d folder is usually used to store and manage sub-configs.
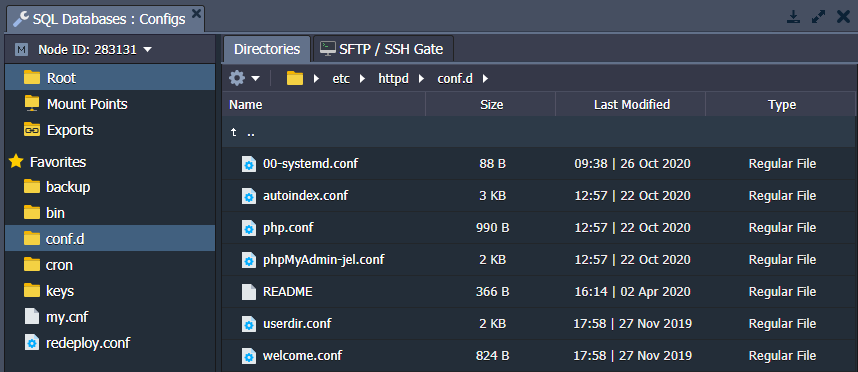
For example, you can access the admin panel configuration file (depends on the database, e.g. phpMyAdmin-jel.conf for MySQL) via the conf.d folder. Use these files to set appropriate criteria for allowing/denying access by IP address or domain.
CONF
The main configuration files of the PostgreSQL database server are located in the /var/lib/pgsql/data folder. For example, it includes configs such as postgresql.conf, pg_hba.conf, pg_ident.conf, etc.
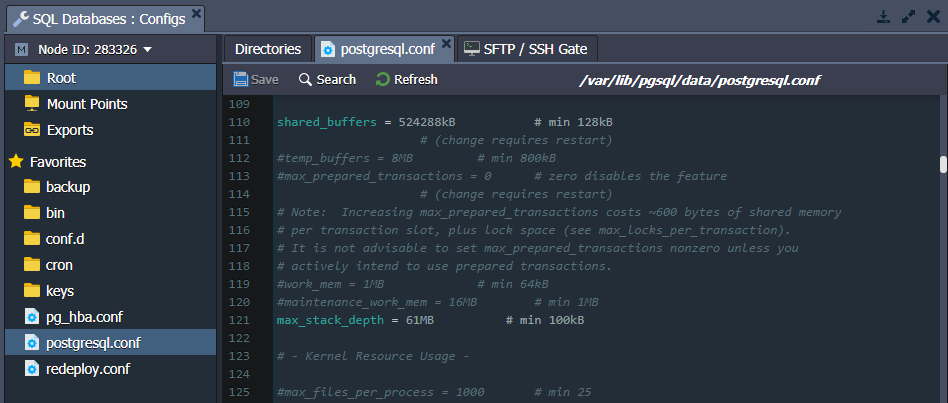
PaaS automatically manages the following two parameters in the /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf file for PostgreSQL databases:
- shared_buffers - calculates as a part of total RAM - quarter if a container has eight or more cloudlets, seventh part otherwise (but not less than 128 KB)
- max_stack_depth - calculates as 1024 subtraction from the maximum stack size (response of the ulimit -s command), converted to MB
If you want to change any of these settings manually, you need to remove the “#Jelastic autoconfiguration mark.” line at the start of the file. Otherwise, your custom changes will be overwritten.